Large-scale open-pit mines extract ores (rocks) with a maximum particle size generally exceeding one meter, while small-scale open-pit mines typically have a particle size of around one meter, and smaller open-pit mines have a particle size of 700-500 millimeters. With such large block sizes, mechanical crushing is necessary to meet the requirements of subsequent production processes.
In recent years, with the development of mining and exploration processes, conveyor belts are used for transporting ores and rocks in order to meet the requirements of belt transportation. Therefore, the ores and rocks need to be crushed to the required size for the conveyor belt.
There are generally three scenarios for the setup of a mining crushing plant:
Coarse crushing outside the open-pit mining area:
Early large-scale open-pit mine crushing plants were mostly located outside the mining area, generally in a safe zone beyond the blast danger limit. So far, the coarse crushing facilities of large and medium-sized open-pit mines in China are all located outside the mining area. Each of these plants has its own characteristics in terms of coarse crushing machine configuration. For example, at the Baotou Bayan Obo iron mine operated by Baosteel, there are two stages of coarse crushing. The first stage uses a 1500 rotary crusher, and the second stage uses four 900 rotary crushers in an overlapping configuration.
Coarse crushing inside the open-pit mining area:
In recent years, foreign open-pit mines have extensively adopted the truck-crushing-conveyor belt transportation process. Some have even employed the truck-slope shaft-crushing-conveyor belt transportation process, which has created favorable conditions for the extraction of large and extra-large open-pit mines. The characteristic of this process is that conveyor belts are the primary transportation tool, enabling high transportation efficiency. However, the crushing machines need to be located within the mining area. This arrangement allows them to handle incoming large-sized materials and crush them to the required granularity for the conveyor belt, transporting the ore to the beneficiation plant and waste rock to the dumping site. Therefore, the crushing machines become an essential component of the mining and exploration process.
Mobile crushing:
Due to the large size and heavy weight of current crushing machines, they can only be fixed on a stable and sturdy foundation. Disassembling and installing them incurs significant costs, making frequent relocation (as mentioned earlier in the semi-fixed crushing scenario) impractical. This limits the flexibility of mining operations. In recent years, some countries have attempted to install large jaw crushers or rotary crushers on mobile frames, which come in two types: wheeled and crawler. They can work in conjunction with electric shovels or front-end loaders. Electric shovels and front-end loaders can directly feed the ore into the crusher (either directly or through feed chutes and heavy-duty plate feeders), and the crushed ore falls onto a movable conveyor belt placed underneath the mobile frame to be transported out of the mining area.
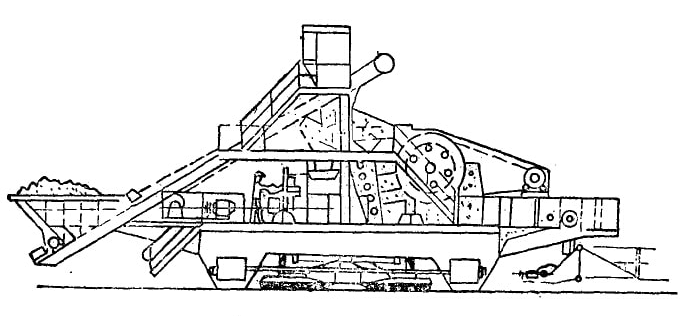
Although the widespread use of such mobile crushing machines is yet to be seen, it is undoubtedly the direction of development for mining and exploration processes.

